Sleep apnea is a common yet often undiagnosed sleep disorder that can have a significant impact on a person’s overall health and well-being. It disrupts normal breathing during sleep, causing the individual to wake up multiple times throughout the night. While sleep apnea can affect anyone, it’s often more prevalent in older adults, those with certain medical conditions, and individuals who are overweight.
In this article, we will explore what sleep apnea is, the different types, its symptoms, and the available treatment options to help manage and improve sleep quality.
What is Sleep Apnea?
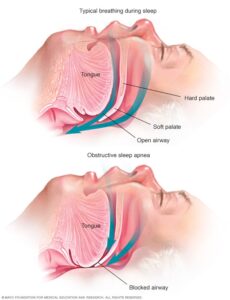
Sleep apnea is a serious sleep disorder in which breathing repeatedly stops and starts during sleep. This disruption can prevent the body from getting enough oxygen and can lead to fragmented sleep, leaving individuals feeling exhausted during the day. It often goes unnoticed because the person may not be aware of the interruptions in their breathing while they sleep.
There are three primary types of sleep apnea:
- Obstructive Sleep Apnea (OSA): This is the most common type of sleep apnea and occurs when the muscles in the throat relax excessively during sleep, causing a temporary blockage of the airway. The brain detects this lack of oxygen and briefly awakens the individual to reopen the airway.
- Central Sleep Apnea (CSA): This type occurs when the brain fails to send the correct signals to the muscles that control breathing. It’s less common than OSA but can still cause significant sleep disturbances.
- Complex Sleep Apnea Syndrome: Also known as treatment-emergent central sleep apnea, this is a combination of obstructive sleep apnea and central sleep apnea. Individuals with this type of sleep apnea experience both the physical obstruction of the airway and irregularities in brain signals.
Symptoms of Sleep Apnea
Sleep apnea can be challenging to diagnose because many of its symptoms occur while the individual is asleep, meaning they may not be fully aware of their condition. However, there are several common signs to watch out for:
- Loud Snoring: While not everyone who snores has sleep apnea, loud, chronic snoring is a common sign of OSA. Snoring occurs when the airway is partially blocked.
- Frequent Pauses in Breathing: A person with sleep apnea may stop breathing for brief periods, often leading to choking or gasping sounds as they resume normal breathing.
- Excessive Daytime Sleepiness: Due to disrupted sleep, individuals with sleep apnea may feel extremely tired during the day, even after a full night’s sleep. This can lead to difficulty concentrating, memory problems, and irritability.
- Morning Headaches: Frequent morning headaches can be a result of low oxygen levels during sleep.
- Dry Mouth or Sore Throat: Waking up with a dry mouth or sore throat is another sign of sleep apnea, as individuals often breathe through their mouth during the night.
- Difficulty Staying Asleep: People with sleep apnea may wake up frequently during the night due to breathing interruptions.
If you or someone you know is experiencing any of these symptoms, it’s important to consult a healthcare provider for an evaluation.
Risks of Untreated Sleep Apnea
Sleep apnea is more than just a nuisance; it can lead to serious health problems if left untreated. Some of the potential risks associated with untreated sleep apnea include:
- Heart Disease: The repeated drops in oxygen levels can strain the heart and lead to high blood pressure, irregular heartbeats, and an increased risk of heart attack or stroke.
- Diabetes: Sleep apnea is linked to an increased risk of developing type 2 diabetes, as it may affect how the body processes insulin.
- Memory and Cognitive Issues: Chronic sleep deprivation caused by sleep apnea can lead to difficulty with concentration, memory loss, and overall cognitive decline.
- Mental Health Issues: The stress and fatigue from untreated sleep apnea can contribute to mood disorders like depression and anxiety.
- Increased Risk of Accidents: Excessive daytime sleepiness makes individuals with sleep apnea more likely to fall asleep during the day, leading to a higher risk of accidents, particularly while driving.
Diagnosis of Sleep Apnea
If you suspect you have sleep apnea, it’s crucial to seek professional medical advice. Diagnosis typically involves a combination of physical examinations, questionnaires about sleep habits, and tests to monitor your breathing during sleep.
- Polysomnography (Sleep Study): A sleep study, either conducted in a sleep clinic or at home, is the most common diagnostic tool. This test records brain waves, oxygen levels, heart rate, and other factors to determine if sleep apnea is present.
- Home Sleep Apnea Test (HSAT): In some cases, a home sleep apnea test may be recommended. It’s a simplified version of a sleep study that can be performed in the comfort of your own home.
Treatment Options for Sleep Apnea
Fortunately, sleep apnea is treatable, and there are several treatment options available, depending on the severity of the condition and the type of sleep apnea diagnosed.
- Lifestyle Changes: For mild cases of sleep apnea, making lifestyle adjustments can significantly improve symptoms. These may include:
- Weight Loss: Losing excess weight can help reduce the severity of obstructive sleep apnea.
- Exercise: Regular physical activity can improve sleep quality and reduce sleep apnea symptoms.
- Avoiding Alcohol and Sedatives: These substances relax the muscles in the throat and can worsen sleep apnea.
- Sleep Positioning: Sleeping on your side instead of your back can help reduce airway obstruction.
- Continuous Positive Airway Pressure (CPAP): CPAP therapy is the most common and effective treatment for moderate to severe obstructive sleep apnea. It involves wearing a mask over the nose (and sometimes the mouth) that delivers a constant stream of air to keep the airway open during sleep.
- Oral Appliances: For mild to moderate sleep apnea, dental devices, also called mandibular advancement devices, can be used to reposition the lower jaw and tongue to keep the airway open.
- Surgery: In some cases, surgery may be necessary to treat sleep apnea. Surgical options include procedures to remove excess tissue from the throat or, in more severe cases, surgery to reposition the jaw.
- Adaptive Servo-Ventilation (ASV): For individuals with central sleep apnea, this advanced form of therapy uses a device to adjust pressure based on detected changes in breathing patterns.
Conclusion
Sleep apnea is a serious disorder that affects millions of people worldwide, but with the right treatment, it can be managed effectively. If you suspect that you or a loved one may be suffering from sleep apnea, it’s important to seek medical advice for an accurate diagnosis and to discuss treatment options. Early intervention can help prevent complications and improve your quality of life, leading to better sleep and overall health.
Contact us for further information!