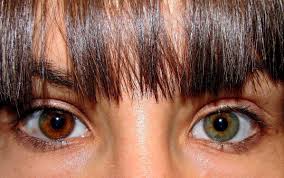
Heterochromia is a rare and captivating condition where a person or animal has two different colored eyes, or sometimes, eyes with different colors within the same eye. This phenomenon is not only visually striking but also comes with a rich history and a variety of causes. Let’s delve into the science, types, and cultural significance of heterochromia, exploring what makes this condition so intriguing.
What is Heterochromia?
Heterochromia, derived from the Greek words hetero meaning “different” and chroma meaning “color,” refers to a disparity in the pigmentation of the eyes. It can appear in two forms: complete heterochromia and sectoral (or partial) heterochromia.
- Complete Heterochromia: This is when each eye is a completely different color. For example, one eye may be blue, while the other is brown or green. It’s the more dramatic form of the condition.
- Sectoral Heterochromia (or Partial Heterochromia): This occurs when one eye has two different colors within the same iris. A person might have a single eye that features a mix of blue and brown, or any other combination of hues.
The Science Behind Heterochromia
The color of the human eye is determined by the amount of melanin in the iris, the colored part of the eye. More melanin results in darker eyes, while less melanin leads to lighter eyes, like blue or green. Heterochromia occurs when there’s an uneven distribution of melanin in one or both eyes.
There are several reasons why someone might develop heterochromia. It can be genetic, congenital, or the result of an injury or illness.
- Genetic Factors: Some people are born with heterochromia due to genetic mutations. This type is usually present at birth and remains throughout life. The condition can run in families, often appearing alongside other inherited traits.
- Congenital Heterochromia: This is present at birth and can be related to genetic conditions such as Waardenburg syndrome or Horner’s syndrome. These conditions cause changes in the melanin production in the eyes, resulting in different colored irises.
- Acquired Heterochromia: In some cases, heterochromia can develop later in life due to an injury or illness. Trauma to the eye can alter its pigmentation, and certain conditions like glaucoma, cataracts, or medication can also lead to changes in eye color.
- Albinism: Albinism, a condition where the body produces little to no melanin, can cause heterochromia in some individuals, especially when it affects the eyes in different ways.
Famous Examples of Heterochromia
While heterochromia is rare in humans, it has captured the public’s imagination, with celebrities, artists, and even fictional characters often sporting eyes of different colors.
- David Bowie is one of the most iconic figures known for his heterochromia. However, his condition was not congenital; rather, it was caused by a traumatic injury that resulted in one of his eyes appearing darker than the other.
- Kate Bosworth, an American actress, is another celebrity with sectoral heterochromia. Her right eye has a striking mixture of blue and brown.
- Mila Kunis also has partial heterochromia, though her eyes appear to be almost the same color, a unique example of how subtle and diverse the condition can be.
In addition to human examples, heterochromia is also common in animals, particularly in dogs and cats. Breeds like the Siberian Husky are well-known for having eyes of different colors, and it’s considered a charming and desirable trait.
Heterochromia in Culture and Mythology
Throughout history, heterochromia has often been a source of fascination. In various cultures, people with different colored eyes were sometimes viewed as being mystical, possessing special powers, or having a unique connection to the spiritual world.
In ancient Egypt, for example, eyes were a powerful symbol of protection and wisdom. The Eye of Horus, which is often depicted as having different colors, was thought to offer protection against evil. Similarly, in folklore, people with heterochromia have sometimes been portrayed as having heightened senses or extraordinary abilities.
Some modern-day subcultures and fandoms have embraced heterochromia as a symbol of beauty and uniqueness. It’s often seen as a desirable characteristic in fantasy or science fiction, with characters featuring strikingly different eye colors to emphasize their otherworldly or supernatural traits.
Is Heterochromia a Medical Concern?
In most cases, heterochromia is not a cause for concern and does not require medical treatment. However, if the condition develops suddenly or is accompanied by other symptoms like pain, vision changes, or discomfort, it’s important to consult a healthcare provider. Acquired heterochromia could be a sign of underlying medical issues that need attention, such as glaucoma or Horner’s syndrome.
Conclusion
Heterochromia is an eye-catching and fascinating condition that has intrigued people for centuries. Whether congenital or acquired, it highlights the beauty of human variation and the complexity of genetic traits. Beyond its scientific and medical significance, heterochromia continues to capture our imagination, appearing in stories, art, and the public consciousness. For those with this unique trait, it is a defining feature that makes them stand out in a world where individuality is celebrated.
Whether you’ve seen it in a friend, a pet, or a famous figure, there’s no denying the captivating allure of heterochromia. It’s a reminder that nature’s beauty comes in many different forms—and sometimes, it’s as simple as two different colored eyes.